Dll1 (基因名), Delta-like protein 1 (蛋白名), dll1_mouse.
产品名称:
Mouse Dll1/ Delta-like protein 1 Recombinant Protein
Delta样蛋白1
货号:
R13897m
商标:
EIAab®
监管等级:
别名:
Drosophila Delta homolog 1, Delta1
序列号:
Q61483
来源:
E.coli
种属:
Mouse
标签:
His
序列:
569-722aa
预估分子量:
16.94 kDa (monomer)
纯度:
Greater than 95% by SDS-PAGE
浓度:
Reconstitution Dependent
形态:
Liquid
内毒素水平:
Please contact protein@eiaab.com The technician for more information.
应用:
存储缓冲液:
50mM NaH2PO4, 500mM NaCl Buffer with 500mM Imidazole, 10%glycerol(PH8.0)
存储:
Store at -20°C. (Avoid repeated freezing and thawing.)
研究领域:
Development Biology
R&D 技术数据
Recombinant mouse Dll1 protein was determined by 12% SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue under reducing conditions.
通用注释
亚单元:
Homodimer (PubMed:12794186). Interacts with TJP1 (PubMed:24715457). Interacts with MMP14; inhibits DLL1-induced Notch signaling (PubMed:21572390). Interacts with MAGI1 (via PDZ domain); forms a complex with CTNNB1 and CDH2 and promotes recruitment to the adherens junction and stabilization on the cell surface (PubMed:15908431). Interacts with PSEN1; undergoes a presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase cleavage that releases a Dll1-intracellular form (PubMed:12794186). Interacts with MFAP5 (PubMed:15788413). Interacts with MIB1 (PubMed:21985982). Interacts with NEURL1B; leads to ubiquitination (PubMed:17003037, PubMed:19723503). Interacts with NEURL1 (PubMed:19723503). Interacts with SYNJ2BP; enhances DLL1 protein stability, and promotes Notch signaling in endothelial cells (By similarity). Interacts with MAGI1, MAGI2, MAGI3 and MPDZ (By similarity). Interacts (via ubiquitin) with EPN1 (via IUM domain); binding with NOTCH1 attached to neighboring cell, promotes ligand ubiquitination and EPN1 interaction, leading to NECD transendocytosis and Notch signaling.
功能:
Transmembrane ligand protein of NOTCH1, NOTCH2 and NOTCH3 receptors that binds the extracellular domain (ECD) of Notch receptor in a cis and trans fashion manner (PubMed:21985982, PubMed:10958687). Following transinteraction, ligand cells produce mechanical force that depends of a clathrin-mediated endocytosis, requiring ligand ubiquitination, EPN1 interaction, and actin polymerisation; these events promote Notch receptor extracellular domain (NECD) transendocytosis and triggers Notch signaling through induction of cleavage, hyperphosphorylation, and nuclear accumulation of the intracellular domain of Notch receptors (NICD) (PubMed:10958687, PubMed:18676613). Is required for embryonic development and maintenance of adult stem cells in many different tissues and immune systeme; the DLL1-induced Notch signaling is mediated through an intercellular communication that regulates cell lineage, cell specification, cell patterning and morphogenesis through effects on differentiation and proliferation (PubMed:17194759, PubMed:19562077, PubMed:18997111, PubMed:23695674, PubMed:16495313, PubMed:21238454, PubMed:22282195, PubMed:7671806, PubMed:17960184, PubMed:22529374, PubMed:19389377, PubMed:23699523, PubMed:19144989, PubMed:23688253, PubMed:23806616, PubMed:26114479, PubMed:22940113, PubMed:25220152, PubMed:20081190, PubMed:21572390, PubMed:22096075). Plays a role in brain development at different level, namely by regulating neuronal differentiation of neural precursor cells via cell-cell interaction, most likely through the lateral inhibitory system in an endogenous level dependent-manner (PubMed:7671806, PubMed:18997111). During neocortex development, Dll1-Notch signaling transmission is mediated by dynamic interactions between intermediate neurogenic progenitors and radial glia; the cell-cell interactions are mediated via dynamic and transient elongation processes, likely to reactivate/maintain Notch activity in neighboring progenitors, and coordinate progenitor cell division and differentiation across radial and zonal boundaries (PubMed:23699523). During cerebellar development, regulates Bergmann glial monolayer formation and its morphological maturation through a Notch signaling pathway (PubMed:23688253). At the retina and spinal cord level, regulates neurogenesis by preventing the premature differentiation of neural progenitors and also by maintaining progenitors in spinal cord through Notch signaling pathway (PubMed:19389377, PubMed:26114479). Also controls neurogenesis of the neural tube in a progenitor domain-specific fashion along the dorsoventral axis (PubMed:20081190). Maintains quiescence of neural stem cells and plays a role as a fate determinant that segregates asymmetrically to one daughter cell during neural stem cells mitosis, resulting in neuronal differentiation in Dll1-inheriting cell (PubMed:23695674). Plays a role in immune systeme development, namely the development of all T-cells and marginal zone (MZ) B cells (PubMed:15146182, PubMed:19217325). Blocks the differentiation of progenitor cells into the B-cell lineage while promoting the emergence of a population of cells with the characteristics of a T-cell/NK-cell precursor (By similarity). Upon MMP14 cleavage, negatively regulates Notch signaling in haematopoietic progenitor cells to specifically maintain normal B-cell development in bone marrow (PubMed:21572390). Also plays a role during muscle development. During early development, inhibits myoblasts differentiation from the medial dermomyotomal lip and later regulates progenitor cell differentiation (PubMed:17194759). Directly modulates cell adhesion and basal lamina formation in satellite cells through Notch signaling. Maintains myogenic progenitors pool by suppressing differentiation through down-regulation of MYOD1 and is required for satellite cell homing and PAX7 expression (PubMed:22940113). During craniofacial and trunk myogenesis suppresses differentiation of cranial mesoderm-derived and somite-derived muscle via MYOD1 regulation but in cranial mesoderm-derived progenitors, is neither required for satellite cell homing nor for PAX7 expression (PubMed:25220152). Also plays a role during pancreatic cell development. During type B pancreatic cell development, may be involved in the initiation of proximodistal patterning in the early pancreatic epithelium (PubMed:22529374). Stimulates multipotent pancreatic progenitor cells proliferation and pancreatic growth by maintaining HES1 expression and PTF1A protein levels (PubMed:22096075). During fetal stages of development, is required to maintain arterial identity and the responsiveness of arterial endothelial cells for VEGFA through regulation of KDR activation and NRP1 expression (PubMed:19144989). Controls sprouting angiogenesis and subsequent vertical branch formation througth regulation on tip cell differentiation (PubMed:22282195). Negatively regulates goblet cell differentiation in intestine and controls secretory fat commitment through lateral inhibition in small intestine (PubMed:21238454, PubMed:21915337). Plays a role during inner ear development; negatively regulates auditory hair cell differentiation (PubMed:16495313). Plays a role during nephron development through Notch signaling pathway (PubMed:23806616). Regulates growth, blood pressure and energy homeostasis (PubMed:19562077).
亚细胞位置:
Dll1-intracellular form
Nucleus
该产品尚未在任何出版物中被引用。
[1].
小鼠Delta样蛋白1(Dll1)重组蛋白是否是无菌的?
蛋白试剂瓶和蛋白保存液是经过高压灭菌的,但也不能保证蛋白是完全无菌的。如果要求蛋白是无菌的,可以用0.2微米的滤器对蛋白进行过滤。
[2].
小鼠Delta样蛋白1(Dll1)重组蛋白的保存缓冲液是什么?
纯化后的蛋白保存在PBS(58mM Na2HPO4, 17mM NaH2PO4, 68mM NaCl, pH7.4)里,并往里面加入500mM咪唑和10%甘油。
[3].
怎样确定小鼠Delta样蛋白1(Dll1)重组蛋白的浓度?
蛋白浓度的确定没有一个统一的标准,这主要取决于蛋白的氨基酸序列。伊艾博是根据不同测试的组合来测定蛋白浓度。考马斯亮蓝法、BCA法、氨基酸序列和氨基酸全序列分析法等都用来测定蛋白浓度。
[4].
小鼠Delta样蛋白1(Dll1)重组蛋白蛋白保存条件是怎样的?
蛋白应保存在 -20℃或 -80℃条件下,为了避免反复冻融,可以将蛋白分装成小份保存。
[5].
小鼠Delta样蛋白1(Dll1)重组蛋白是否可以用于活体实验?
重组蛋白没有用于任何的活体实验,因此蛋白的活性和半衰期是不确定的。
[6].
小鼠Delta样蛋白1(Dll1)重组蛋白的保质期是多久?
在适当的保存条件下,从购买之日起蛋白可以稳定保存6-12个月。适当的保存条件是:蛋白保存在-20°C o或 -80℃,保证蛋白的保存浓度高于0.1mg/ml,限制蛋白反复冻融的次数。我们公司常规的质量检测保证所有产品在销售时都有可接受的生物活性。但是我们不能控制终端用户蛋白的保存条件。如果产品在有效期内出现问题,请联系我们的技术支持。
[7].
你们蛋白和抗体的报价是怎么样的?
我们将根据你需要的蛋白和抗体的大小进行报价。
[8].
小鼠Delta样蛋白1(Dll1)重组蛋白是否能够提供蛋白片段?
我们现有的人的蛋白的序列可以有很多。你可以选择你感兴趣的靶向部分,我们将会按您的需求提供蛋白和抗体。
[9].
小鼠Delta样蛋白1(Dll1)重组蛋白的货期或发货时间一般是多长?
具体指标的货期需要确定。最快一周,最长可能一个月。
反馈墙
评论数 : 0
所有用户
所有用户
默认排序
默认排序
最近
早期
目前还没有评论。



通知
规格
数量
单价 (¥)
小计 1 (¥)
小计 2:
¥

规格
数量
单价 (¥)



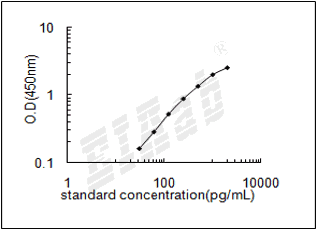

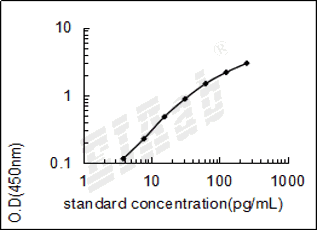
 验证序列:
验证序列:



 折扣:
折扣: