LEP (基因名), Leptin (蛋白名), lep_human.
产品名称:
Human LEP/ Leptin Recombinant Protein
瘦素
货号:
R0084h
商标:
EIAab®
监管等级:
别名:
Obese protein, Obesity factor, OB, OBS
序列号:
P41159
来源:
E.coli
种属:
Human
标签:
His
序列:
22-167aa
预估分子量:
16.06 kDa (monomer)
纯度:
>90% by SDS-PAGE
浓度:
Reconstitution Dependent
形态:
Liquid
内毒素水平:
Please contact protein@eiaab.com The technician for more information.
应用:
存储缓冲液:
50mM NaH2PO4, 500mM NaCl Buffer with 500mM Imidazole, 10%glycerol(PH8.0)
存储:
Store at -20°C. (Avoid repeated freezing and thawing.)
研究领域:
Metabolism
R&D 技术数据
The PCR product of human LEP gene was determined by 1% Agarose stained with EB.
Recombinant human LEP protein was determined by 12% SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue under reducing conditions.
基因位点
LEP Gene in genomic location: bands according to Ensembl, locations according to GeneLoc (and/or Entrez Gene and/or Ensembl if different)
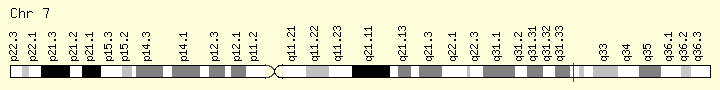
通用注释
亚单元:
Interacts with SIGLEC6.
功能:
Key player in the regulation of energy balance and body weight control. Once released into the circulation, has central and peripheral effects by binding LEPR, found in many tissues, which results in the activation of several major signaling pathways (PubMed:17344214, PubMed:15899045, PubMed:19688109). In the hypothalamus, acts as an appetite-regulating factor that induces a decrease in food intake and an increase in energy consumption by inducing anorexinogenic factors and suppressing orexigenic neuropeptides, also regulates bone mass and secretion of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal hormones. In the periphery, increases basal metabolism, influences reproductive function, regulates pancreatic beta-cell function and insulin secretion, is pro-angiogenic for endothelial cell and affects innate and adaptive immunity (By similarity) (PubMed:8589726, PubMed:11460888, PubMed:19688109, PubMed:24340098, PubMed:25060689). In the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus, activates by depolarization POMC neurons inducing FOS and SOCS3 expression to release anorexigenic peptides and inhibits by hyperpolarization NPY neurons inducing SOCS3 with a consequent reduction on release of orexigenic peptides (By similarity). In addition to its known satiety inducing effect, has a modulatory role in nutrient absorption. In the intestine, reduces glucose absorption by enterocytes by activating PKC and leading to a sequential activation of p38, PI3K and ERK signaling pathways which exerts an inhibitory effect on glucose absorption (PubMed:24340098). Acts as a growth factor on certain tissues, through the activation of different signaling pathways increases expression of genes involved in cell cycle regulation such as CCND1, via JAK2-STAT3 pathway, or VEGFA, via MAPK1/3 and PI3K-AKT1 pathways (By similarity) (PubMed:17344214). May also play an apoptotic role via JAK2-STAT3 pathway and up-regulation of BIRC5 expression (PubMed:18242580). Pro-angiogenic, has mitogenic activity on vascular endothelial cells and plays a role in matrix remodeling by regulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) (PubMed:11460888). In innate immunity, modulates the activity and function of neutrophils by increasing chemotaxis and the secretion of oxygen radicals. Increases phagocytosis by macrophages and enhances secretion of pro-inflammatory mediators. Increases cytotoxic ability of NK cells (PubMed:12504075). Plays a pro-inflammatory role, in synergy with IL1B, by inducing NOS2 wich promotes the production of IL6, IL8 and Prostaglandin E2, through a signaling pathway that involves JAK2, PI3K, MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAPK14/p38 (PubMed:15899045, PubMed:19688109). In adaptive immunity, promotes the switch of memory T-cells towards T helper-1 cell immune responses (By similarity). Increases CD4(+)CD25(-) T-cell proliferation and reduces autophagy during TCR (T-cell receptor) stimulation, through MTOR signaling pathway activation and BCL2 up-regulation (PubMed:25060689).
亚细胞位置:
Secreted
[1].
A Bilgiç, M B Oflaz, T Baysal, et al.
[2].
Ç Ç Sadıç, A Bilgiç, İ Kılınç, et al.
[4].
Kornicka K, Marycz K, Tomaszewski K A, et al.
[1].
"Genetic variation at selected SNPs in the leptin gene and association of alleles with markers of kidney disease in a Xhosa population of South Africa."
[2].
"G(-2548)A leptin gene polymorphism in obese subjects is associated with serum leptin concentration and bone mass."
[3].
"Leptin gene -2548G/A variants predict risperidone-associated weight gain in children and adolescents."
[4].
"Genetic correlates of olanzapine-induced weight gain in schizophrenia subjects from north India: role of metabolic pathway genes."
[5].
"Leptin and leptin receptor gene polymorphisms and increases in body mass index (BMI) from olanzapine treatment in persons with schizophrenia."
[6].
"Association of clozapine-induced weight gain with a polymorphism in the leptin promoter region in patients with chronic schizophrenia in a Chinese population."
[7].
"Site -2548 of the leptin gene is associated with gender-specific trends in newborn size and cord leptin levels."
[8].
"Signalling pathway involved in nitric oxide synthase type II activation in chondrocytes: synergistic effect of leptin with interleukin-1."
[9].
"Leptin and leptin receptor gene polymorphisms and changes in glucose homeostasis in response to regular exercise in nondiabetic individuals: the HERITAGE family study."
[10].
"Potential role of leptin in angiogenesis: leptin induces endothelial cell proliferation and expression of matrix metalloproteinases in vivo and in vitro."
[1].
人瘦素(LEP)重组蛋白是否是无菌的?
蛋白试剂瓶和蛋白保存液是经过高压灭菌的,但也不能保证蛋白是完全无菌的。如果要求蛋白是无菌的,可以用0.2微米的滤器对蛋白进行过滤。
[2].
人瘦素(LEP)重组蛋白的保存缓冲液是什么?
纯化后的蛋白保存在PBS(58mM Na2HPO4, 17mM NaH2PO4, 68mM NaCl, pH7.4)里,并往里面加入500mM咪唑和10%甘油。
[3].
怎样确定人瘦素(LEP)重组蛋白的浓度?
蛋白浓度的确定没有一个统一的标准,这主要取决于蛋白的氨基酸序列。伊艾博是根据不同测试的组合来测定蛋白浓度。考马斯亮蓝法、BCA法、氨基酸序列和氨基酸全序列分析法等都用来测定蛋白浓度。
[4].
人瘦素(LEP)重组蛋白蛋白保存条件是怎样的?
蛋白应保存在 -20℃或 -80℃条件下,为了避免反复冻融,可以将蛋白分装成小份保存。
[5].
人瘦素(LEP)重组蛋白是否可以用于活体实验?
重组蛋白没有用于任何的活体实验,因此蛋白的活性和半衰期是不确定的。
[6].
人瘦素(LEP)重组蛋白的保质期是多久?
在适当的保存条件下,从购买之日起蛋白可以稳定保存6-12个月。适当的保存条件是:蛋白保存在-20°C o或 -80℃,保证蛋白的保存浓度高于0.1mg/ml,限制蛋白反复冻融的次数。我们公司常规的质量检测保证所有产品在销售时都有可接受的生物活性。但是我们不能控制终端用户蛋白的保存条件。如果产品在有效期内出现问题,请联系我们的技术支持。
[7].
你们蛋白和抗体的报价是怎么样的?
我们将根据你需要的蛋白和抗体的大小进行报价。
[8].
人瘦素(LEP)重组蛋白是否能够提供蛋白片段?
我们现有的人的蛋白的序列可以有很多。你可以选择你感兴趣的靶向部分,我们将会按您的需求提供蛋白和抗体。
[9].
人瘦素(LEP)重组蛋白的货期或发货时间一般是多长?
具体指标的货期需要确定。最快一周,最长可能一个月。
反馈墙
评论数 : 0
所有用户
所有用户
默认排序
默认排序
最近
早期
目前还没有评论。



通知
规格
数量
单价 (¥)
小计 1 (¥)
小计 2:
¥

规格
数量
单价 (¥)



 验证序列:
验证序列:



 折扣:
折扣: